No matter where you look, there are myths and misconceptions about plant based diets. But, rest assured, there are also a lot of truths, facts and benefits of adopting a vegan diet.
From overall health improvements to protecting the environment and avoiding animal cruelty, but how does going plant based affect your training?
Can a plant based diet support muscle and strength building?
We take a closer look.
Can you be vegan and build muscle?

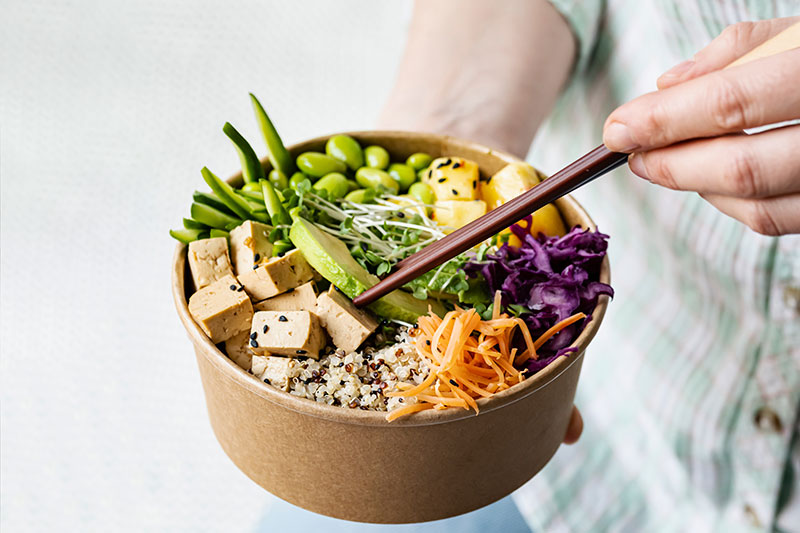
Wondering if can you build muscle on a vegan diet is a pretty common query for keen bodybuilders. Although a plant based diet isn’t really anything new, there has certainly been an increase in veganism in recent years.
But how does a plant based diet affect muscle and strength? Can you be vegan and hit your body goals? Well, of course, you can.
The trick is knowing how to transition to a vegan diet and support your bulking (or cutting) goals, especially if you haven’t always followed a plant based diet. And let’s face it, the Internet is full of weird and wonderful things, but it doesn’t always help you to gain clarity on popular subjects (such as veganism) when there is so much damn information around.
In response to the popular question ‘can you build muscle on a vegan diet?’ the answer is a big fat yes. But there’s plenty more to be said on the topic.
Here’s how to optimize your vegan diet for strength building
Following a plant based diet and building muscle and strength shouldn’t have to feel like an uphill battle. However, it is important to ensure your nutrition supports your fitness, overall health and physique goals.
Going vegan and building muscle? No problem, follow these tips to optimize your plant based diet.
Master your nutrition quality
Whether vegan or not, the quality of your food should be your number one priority when building muscle and strength. We cannot guage this by protein or calories, however, which is why it’s important to understand foods in their natural state.
We may be stating the obvious here, but a veggie and tofu stiry fry is far healthier than a takeaway of dirty fries and a side of cookies. Just because you’re following a plant based diet, it doesn’t mean you can start bingeing ‘vegan’ fast foods (such as fries), especially if you’re trying to bulk up.
The same applies to plant based snacks. Opt for an apple with almond butter over a bag of cookies. Catch my drift? Sure, these can be treat foods (or eaten in cheat meals), but the quality is important here in order to hit your goals.
By eating a variety of whole foods, you can rest assured your body is hitting its macronutrient goals, as well as fiber, vitamins and other minerals. Where possible, opt for fresh veggies and fruit over processed ‘vegan foods’ that can be thrown in the oven.
Understand calories
Calories are a measure of the energy that we get from food. Eating the right amount of calories is important for both athletic performance and physique goals.
If you struggle to keep on top of your calorie intake, consider using a calorie tracking app to help you hit your daily target. However, don’t get too hung up on the numbers, since calorie tracking is often an estimate. Your calorie intake kinda comes second after the quality of the food you’re eating, to ensure that you’re consuming enough energy to support your weight training goals.
Also Read: What are the best protein pills?
To find out how many calories you need to consume each day, you first need to determine your BMR (basal metabolic rate). We’ve got another post on all that ‘must’ stuff, but here’s a quick breakdown:
- Women: 655 + (4.3 x weight in lbs.) + (4.7 x height in inches) – (4.7 x age in years) = BMR
- Men: 66 + (6.3 x body weight in lbs.) + (12.9 x height in inches) – (6.8 x age in years) = BMR
Once you’ve got this number, we can then work out your estimated calorie intake by adding another variable…
If you’re about to start a regular weight training routine, it’s understandable that you would factor in this higher level of activity to make sure that you’re eating enough calories to support your muscle growth.
- Sedentary = x1.0
- Very light activity = x1.2
- Light activity = x1.4
- Moderate activity = x1.6
- High activity = x1.8
- Extreme activity = x2.0
Hit your macros
Now that you know your vegan diet for building muscle is packed with nutritious foods, and you’re hitting the right number of calories, we move onto macronutrients (aka, macros). These are nutrients our bodies need in the largest amounts: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each one has a different function in our bodies.
Typically, vegan bodybuilders aim to get around 50% of their calories from carbs (whole, nutrient-dense where possible), 25 to 30% of calories from healthy fats (think avocado, but more on that later) and 20 to 25% from protein. If you’re an endurance athlete, for example, you’ll need more carbohydrates, and not quite as much protein. If you’re a competitive strength athlete, you’ll likely need more protein.
Micronutrients, however, include:
- Water
- Minerals – Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Iron, Zinc, Copper
- Fat-soluble vitamins – Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K
- Water-soluble vitamins – Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, vitamin B9 (B9), Vitamin C
Popular safe and legal steroid alternatives
Know your go-to sources of protein

If you’re considering switching to a plant based diet, one of the most common concerns from gym-goers is their protein intake. Whether you’re looking to compete in bodybuilding, or simply looking to gain a little extra muscle – protein is important. Especially if you want to achieve a chiselled physique.
High-level vegan strength athletes need around 1.8 to 2.5 grams of protein per kilogram of bodyweight. If your training is a little less intense, you won’t quite need as much, however.
And so, whether you’ve recently gone vegan or are considering making the leap, knowing where to get protein is going to be key to hitting your gym goals.
High-protein vegan foods:
- High-protein pastas (such as edamame, red lentil, chickpea, black bean)
- Seitan
- Soy curls
- Tempeh
- Textured vegetable protein (TVP)
- Tofu
- Nutritional yeast
- Hemp hearts
- Chia seeds
Know your pre and post-workout foods
For vegans looking to build strength, slow-digesting carbs and a moderate amount of protein pre-workout can support your fitness goals, with faster-digesting carbs and more protein supporting your recovery post-workout.
For example, oatmeal with soy milk and hemp hearts pre-workout, and an apple with a protein shake post-workout.
The ultimate plant based weight training meal plan

If you’re looking to make the switch to a plant based diet, or simply need a nudge in the right direction to conquer your body goals, we’ve got the ultimate plant based weight training meal plan for you to follow.
While veganism is pretty easy for many new plant based eaters to follow, it can be a huge change for some. Trust us; if you get the planning out of the way now, then you’ll have a much easier time sticking to your new lifestyle (and ultimately get better results).
What plant based foods should you eat while weight training?
Long gone are the myths that a plant based diet is bland, boring, or limited to eating salads. While some foods are ‘accidentally’ vegan, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll get enough nutrition from vegan junks foods, for example.
Also Read: What are cheat meals and refeed days?
Since your macronutrients are super important for building muscle, we’re going to go through each in a little more detail with some suggested vegan foods for muscle building.
Plant based macro sources
Whether you’re a meat-eater or you’re following a plant based diet, your carb intake is incredibly important if you want to build muscle and strength.
Suggest vegan foods for carbs:
- Sweet potatoes (iron, calcium, selenium, B vitamins (multiple), vitamin C)
- Brown rice (fibre, calcium, iron, sodium, magnesium, selenium, folate)
- Lentils (fibre, vitamin B1e, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B5, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper, manganese)
- Quinoa (manganese, phosphorus, copper, folate, iron, magnesium, zinc, thamin, vitamin B6)
- Oats (manganese, phosphorus, copper, vitamin B1, iron, selenium, magnesium, zinc)
- Bananas (potassium, vitamin B6, vitamin C, magnesium, copper, manganese, fibre)
- Chickpeas (vitamin B6, folate, vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5)
- Kidney beans (folate, thiamin, vitamin K, vitamin B6, vitamin C, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, and vitamin B5)
- Beetroot (vitamin B9, fibre, manganese, potassium, iron, vitamin C, vitamin B9)
Plant based protein sources for muscle building:
- Tofu (calcium, iron, potassium, manganese, selenium, phosphorus, magnesium, copper, zinc, vitamin B)
- Tempeh (sodium, iron, calcium, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, magnesium, phosphorus, manganese)
- Seitan (selenium, iron, phosphorus, calcium, copper)
- Lentils (fibre, vitamin B1e, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B5, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper, manganese)
- Edamame (calcium, vitamin C, iron, vitamin K, folate)
- Chickpeas (vitamin B6, folate, vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5)
- Quinoa (manganese, phosphorus, copper, folate, iron, magnesium, zinc, thamin, vitamin B6)
- Nutritional yeast (vitamin B1e, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, zinc, selenium, manganese)
- Oats (manganese, phosphorus, copper, vitamin B1, iron, selenium, magnesium, zinc)
- Soy milk (fibre, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, vitamin B9, vitamin B12, vitamin A, vitamin E)
- Hempseed (calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, folate, vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin E)
- Chia seeds (fibre, calcium, manganese, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, vitamin B3, potassium, vitamin B1, vitamin B2)
- Green peas (fibre, protein, vitamin A, vitamin K, vitamin C, vitamin B1, folate, manganese, iron, phosphorus)
- Beans (most varieties) (As an example, pinto beans contain: fibre, iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, folate, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin E, vitamin K)
- Nuts (As an example, cashew nuts contain: fibre, copper, magnesium, manganese, zinc, phosphorus, iron, selenium, vitamin B1, vitamin K, vitamin B6)
Plant based (healthy) fat sources for muscle building:
- Avocado (vitamin B5, fibre, folate, vitamin K, copper, vitamin B2, potassium, vitamin E, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin C, magnesium, manganese, thiamin, iron)
- Coconut (fibre, manganese, selenium, copper, phosphorus, potassium, iron, zinc)
- Chia seeds (fibre, calcium, manganese, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, vitamin B3, potassium, vitamin B1, vitamin B2)
- Flax seeds (fibre, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, folate, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium)
- Pumpkin seeds (fibre, vitamin K, phosphorus, manganese, magnesium, iron, zinc, copper)
- Almonds (fibre, vitamin E, manganese, magnesium, copper, vitamin B2, phosphorus)
- Cashew nuts (fibre, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc)
- Walnuts (fibre, calcium, iron, sodium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamin B6)
- Brazil nuts (fibre, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, zinc, iron, sodium)
Vegan weight training meal plan example
Not sure how to kickstart your new plant based weight training? We’ve got a kickass combination from some of the above foods, to support your workouts and encourage muscle growth.
Monday
- Breakfast: Vegan yoghurt, oats, strawberries, banana slices, and honey
- Lunch: Tofu sandwich with wholemeal bread, avocado, onion, tomato, and rocket
- Snack: Peanut butter and oatmeal snack bars
- Dinner: Seitan beef burger, jacket sweet potato, and salad (leafy greens)
Tuesday
- Breakfast: Porridge with soy milk, vegan protein powder, blueberries, and flaked almonds
- Lunch: Vegan burrito bowl with rice, kidney beans, and vegan mince
- Snack: Apple slices and peanut butter
- Dinner: Rice, tofu, and asparagus (with your choice of sauce and seasoning)
Wednesday
- Breakfast: Tofu scramble on sourdough or wholemeal bread
- Lunch: Chickpea and butternut squash salad
- Snack: Vegan chocolate and peanut butter protein shake
- Dinner: Vegan protein chilli with mixed beans
Thursday
- Breakfast: Smoothie made with almond milk, frozen banana, mango, spinach, pumpkin seeds, and vegan protein powder
- Lunch: Lentil and black bean soup
- Snack: Watermelon slices, and cashew nuts
- Dinner: Vegan yellow curry with tempeh
Friday
- Breakfast: Vegan protein pancakes, strawberries, blueberries, and syrup
- Lunch: Vegan tempeh BLT
- Snack: Strawberries, blueberries, and dark chocolate
- Dinner: Salt and pepper tofu with stir-fry veg
Saturday
- Breakfast: Granola with soy milk and vegan protein powder
- Lunch: Coconut and tofu stir-fry with noodles
- Snack: Vegan cheese slices with oatcakes
- Dinner: Butternut lentil curry and brown rice
Sunday
- Breakfast: Breakfast burrito with tofu, beans, brown rice, and veggies
- Lunch: Lentil veggie stew
- Snack: Apple slices with almond butter
- Dinner: Sweet potato skins (vegan cheese, pumpkin seeds), avocado, and beetroot
Remember to adjust your portions accordingly depending on how many calories you should be consuming.
Workouts to support your plant based muscle building diet

Whether you’re getting started with olympic weighlifting, competing in strongman or powerlifting, a plant based diet for muscle building (and strength) doesn’t necessarily mean that your workouts have to change.
Also Read: How much protein should you eat per day?
We’ve got a bunch of back workouts, workouts to get bigger legs, bigger arm workouts and cardio for bodybuilding to get you started.
Mistakes worth avoiding when following a plant based muscle building diet
If you’re considering going vegan while building muscle, it’s not uncommon to make one of the following mistakes initially. Newbie vegans aren’t always aware of how awesome a plant based diet can be – even for those looking to build muscle.
But before you get stuck in, here are some mistakes worth looking for (and avoiding!):
- Cutting out animal products with no replacement – If you’re taking out animal products and not replacing these nutrients, you could end up deficient in a number of things. Looking for a variety of whole, plant based foods that work well as alternatives.
- Focus on what you can’t eat – Instead of worrying about the animal based foods you’ve left behind, start to think about what you can have and get a little creative with plant based foods instead.
- Don’t get caught up in foods that are accidentally vegan, thinking they must be good for you. There are plenty of junk and processed foods that are actually vegan. These won’t necessarily support your training goals, though!